Melinda Turani, Gaspar Banfalvi, Krisztina Kukoricza, Judit Jakim, Istvan Pocsi, Adam Kemeny-Beke and Gabor Nagy
To evaluate the potential of silver and gold nanoparticles in the healing of cornea damages cell regeneration was tested. Corneal limbal cell regrowth and structural changes in chromatin structure were studied in the presence of silver (AgNPs, 10 nm) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs, 100 nm). An in vitro cell scratch model served to follow limbal cell growth by long-term scanning micro-photography. AgNPs exerted only a moderate delay on cell regeneration. Low concentration (80 ppm) of AuNPs did not affect severely, 160 and 320 ppm extended the repopulation of limbal monolayer in a included: a) decondensed veil-like, b) fibrillary chromatin, c) supercoiled ribbon structures, d) visible chromosomes as chromatin bodies, e) early linear forms, and e) finally as metaphase chromosomes. Characteristic distortions in chromatin structures took place in nuclei in the presence of nanoparticles. Ag nanoparticles prevented the formation of linear and metaphase chromosomes. Gold particles (80 ppm) allowed the formation of chromatin bodies, but not more condensed chromosomal forms. Higher concentrations of AuNPs prevented the formation of ribboned chromatin and higher chromosomal structures. Results show that cell regeneration and chromatin toxicity are dose dependent. In spite of their lower size, Ag nanoparticles (10 nm) were less toxic than larger Au particles (100 nm).
Elegbede Isa Olalekan, Fatima Kies, Lawal-Are Aderonke Omolara, Salau Damilola Rashidat, Fashina-Bombata Hakeem, Akintola Shehu Latunji, Aderolu Ademola Zaid, Ndimele Emeka, Onyema Ikenna Charles and Fadeyi Oluwaseun
This study examines the effect of physicochemical parameters on different categories of fish species; benthopelagic, pelagic and demersal on Lake Volta. The methods of this study were based on the estimation of hydrographic data, collection and analysis of physicochemical parameters of the water samples. Fish samples were collected from four sampling stations namely Oti River at Sabra, White Volta at Daboya, Black Volta at Bamboi and Lower Volta at Amedeka. This review work studies a study which was carried out between February 1995 and January, 1996. A statistical analysis was conducted. Water resource availability and mean annual rainfall of Lake Volta were highest in Black Volta and Oti River respectively. The results show pH 194-520, Conductivity (μS cm-1), Dissolved oxygen 8.0- 11.2 (mg/L), Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) 2.7-105 (mg/L), Alkalinity 35.3-53.8 (mg/L), Chloride 4.6-13.6 (mg/L), Calcium 4.8-10.1 (mg/L), Total Hardness 17.4-44.1 (mg/L), Magnesium 2.5-8.3 (mg/L), Ammonia-N 0.4-1.6 (mg/L), Phosphate 0.2-0.9 (mg/L), Nitrate 0.2-6.6 (mg/L), Nitrite 0.06-0.6 (mg/L) and Sulfate 1.2-8.9 (mg/L) respectively. The benthopelagic, pelagic and demersal fish population show 16, 6 and 11 number of different fish species respectively in the lake. The study concludes that the quality of the water is satisfactory when compared with other lakes. Anthropogenic activities is insignificant on the aquatic habitat and the appreciable fish population is an indication of good biological quality of the water body.
Annalicia Vaughan, Svetlana Stevanovic, Leanne E Morrison, Ali Mohammad Pourkhesalian, Mostafizur Rahman, Ali Zare, Branka Miljevic, Felicia Goh, Vandana Relan, Rayleen V Bowman, Kwun M Fong, Steven E Bottle, Zoran D Ristovski and Ian A Yang
Background: Exposure to air pollutants, including diesel particulate matter, has been linked to adverse respiratory health effects. Inhaled diesel particulate matter contains adsorbed organic compounds. It is not clear whether the adsorbed organics or the residual components are more deleterious to airway cells. Using a physiologically relevant model, we investigated the role of diesel organic content on mediating cellular responses of primary human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) cultured at an air-liquid interface (ALI). Methods: Primary HBECs were cultured and differentiated at ALI for at least 28 days. To determine which component is most harmful, we compared primary HBEC responses elicited by residual (with organics removed) diesel emissions (DE) to those elicited by neat (unmodified) DE for 30 and 60 minutes at ALI, with cigarette smoke condensate (CSC) as the positive control, and filtered air as negative control. Cell viability (WST-1 cell proliferation assay), inflammation (TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-8 ELISA) and changes in gene expression (qRT-PCR for HO-1, CYP1A1, TNF-α and IL-8 mRNA) were measured. Results: Immunofluorescence and cytological staining confirmed the mucociliary phenotype of primary HBECs differentiated at ALI. Neat DE caused a comparable reduction in cell viability at 30 or 60 min exposures, whereas residual DE caused a greater reduction at 60 min. When corrected for cell viability, cytokine protein secretion for TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-8 were maximal with residual DE at 60 min. mRNA expression for HO-1, CYP1A1, TNF-α and IL-8 was not significantly different between exposures. Conclusion: This study provides new insights into epithelial cell responses to diesel emissions using a physiologically relevant aerosol exposure model. Both the organic content and residual components of diesel emissions play an important role in determining bronchial epithelial cell response in vitro. Future studies should be directed at testing potentially useful interventions against the adverse health effects of air pollution exposure.
Pierluigi Cocco, Mariagrazia Zucca, Sonia Sanna, Giannina Satta, Emanuele Angelucci, Attilio Gabbas, Maria Monne, Marcello Campagna, Aldo Scarpa and Maria Grazia Ennas
Background: Gene-environment interactions are suggested to play a role in lymphomagenesis. Methods: We tested the interaction between the NAT1/NAT2 phenotype, as inferred by the respective genotypes, and exposure to dietary and lifestyle risk factors, in 199 incident lymphoma cases and 188 population controls. We used unconditional logistic regression to calculate the odds ratio (OR) and its 95% confidence interval for lymphoma (all subtypes combined) and B cell lymphoma, associated to the rapid NAT1 phenotype and to the intermediate and slow NAT2 phenotype, and to the estimated dietary intake of heterocyclic amines and folate, current smoking, coffee, and use of permanent hair dyes, as well as the respective interaction terms. We adjusted the ORs by age, gender, and education, and we used the likelihood ratio test to test the interaction between the NAT1, NAT2 phenotype and the dietary and lifestyle variables. Results: We observed an increase in risk of lymphoma (all subtypes combined) and B-cell lymphoma in particular associated with the estimated above median dietary intake of heterocyclic amines (OR = 4.2, 95%CI 1.2 – 14.8) and folate (OR = 4.1, 95%CI 0.7 – 22.4) among subjects with the NAT1 rapid acetylator phenotype, but not independent on the NAT1 phenotype. The test for interaction was significant for heterocyclic amines, but not for folate (p for interaction = 0.026 and 0.076 respectively). Ever use of permanent hair dyes was associated with an elevated risk independent on the NAT1, NAT2 phenotypes; risk decreased to null among intermediate and slow NAT1 acetylators (p for interaction = 0.010). Conclusions: Our results suggest that NAT1, NAT2 polymorphisms interact with dietary and lifestyle exposures in modulating risk of lymphoma and particularly B-cell lymphoma.
Varinlioglu A, Turhan S and Karatasl M
The uptake of radioactive cesium by mussels, Mytilus galloprovincialis, collected from Marmara Sea exposed over one month to radioactive contaminated sea water and the subsequent loss in non-radioactive sea water were studied with 137Cs. The uptakes and losses of 137Cs by mussels observed experimentally were plotted and fit to appropriate functions. The experiments clearly showed that the activity concentrations of 137Cs in mussels reached a peak which is a saturation state in 30 days while the loss of a substantial of the 137Cs activity by mussels was observed within 15 days. The activity concentrations of 137Cs in soft parts of the mussels were higher than those measured in whole body of the mussels.
Wondimagegne Asefa and Tarekegn Beranu
The levels of trace metals (Cd, Co, Cu, Mn, Fe, Pb, Zn, Cr and Ni) in three commercially important fish tissues and their environment of a newly constructed manmade dam, Tendaho reservoir, investigated using validated analytical method under appropriate quality control measures. The analysis result of samples after wet digestion with flame atomic absorption spectroscopy showed that excluding Zn, Mn and Co (fishes tissue>sediment>water) metals distribution in fishes tissue and their environment existed in the order of: sediment>fishes tissue>water. In fish species regardless of the type, the levels of almost all metals were higher in detoxification organs (gill and liver) than in muscle. Higher values of calculated bioconcentration factor and two-way ANOVA analysis result (P-value<0.05) also indicated that the highest level of majority metals existed in Catfish in compared to Tilapia and Barbus intermedius. The concentrations of Mn, Fe, Pb and Cr were higher than Ethiopian Environmental Protection Authority (2003) guidelines in water while the levels of all metals were below PEL guidelines of USEPA (2000) for sediment. Safety of customers from trace metal pollution hazard from fishes was indicated by low level of calculated hazard quotient and comparisons result with WHO (1989) and USFDA (1993) guideline values.
Khandakar Akhter Hossain
This paper deals with the status of ship-recycling industry in Bangladesh in compare to world and which has received considerable attention during last two decades. The social and environmental impacts of the ship recycling in Bangladesh have also been covered. Considering its positive economical contribution as well as some negative effect like lack of occupational health and safety standard, the research has made to address whether Bangladesh should continue supporting this business on their soil. Few very viable and important statistics, fact and figure has shown and analyzed for local recycling industry as a whole. Some viable recommendations are made at the conclusion.
Orabi H Orabi and Mahmoud F Osman
The value of environmental health and the functioning of ecosystems are widely recognized at the Manzala Lagoon for the first time and are becoming more familiar to illuminated public opinions. The freshwater molluscs play significant roles in the public and veterinary health in the Manzala Lagoon region. The abundance of freshwater gastropods species Biomphalaria alexandrina, B. glabrata, Bellamya unicolor, Viviparous contectus, Bulinus (Bulinus) truncatus, Lymnaea columella, L.(Galba) truncatula, Melanoides maculate, M. tuberculata, Planorbis planorbis, Succinea (Amphibina) cleopatra, Theodoxus (Neritaea) niloticus and T. (N.) anatolicus was negatively correlated with salinity. These gastropods are of considerable importance because they are hosts for Cercaria pusilla, Fasciola hepatica, Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma haematobium disease vectors. The latter two can cause Schistosomiasis transmission (Bilharzia). People living along the banks of the drains which are located in southern and western sectors of the Manzala Lagoon are exposed to chemical pollutants. The drains wastewater pollutants affected the human health because they use the drain waters in their life needs.
Pirbazari AE, Pargami NR, Ashja N and Emami MS
This paper reports on the development of organo-modified tea waste (TW) adsorbent prepared by using sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) for removing methylene blue (MB), a model cationic dye, from aqueous solution. The natural and modified samples were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), nitrogen physisorption and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). Batch adsorption experiments were carried out to remove MB from its aqueous solutions using SDS coated TW (SCTW). Analysis of adsorption results obtained at different temperatures showed that the adsorption pattern on the SCTW can be described perfectly with Langmuir isotherm model compared with Freundlich isotherm model. The adsorption process has been found exothermic in nature and thermodynamic parameters have been calculated. The adsorption kinetic followed the pseudo-second order kinetic model. Desorption studies suggest that MB adsorption onto the SCTW should be mainly controlled by the hydrophobic interaction mechanism, along with a considerable contribution of the cationic exchange mechanism.
Meseret Muche, Addis Kokeb and Eyayu Molla
The economies for most developing countries primarily depend on agriculture. Studying the physicochemical properties of soil is important for sustainable management of the agricultural resources and economic growth. Soil acidity is one of the main reasons for nutrient depletion as well as causes of fertility decline that affects crop production. The main objective of this investigation is to assess the acidity status and physicochemical properties of soil in different land use types in Alket Wonzi Watershed, Farta district, Northwest Ethiopia. Soil samples were taken at 0-25 cm depth, on four land use types viz., natural forest, cultivated land, plantation forest and grazing land. The result soils in the natural forest had significantly (p<0.05) higher soil pH and lower exchangeable acidity (p<0.01). Similarly, significantly higher (p<0.01) exchangeable bases (Ca2+, Mg2+, K+), total nitrogen, organic matter, available potassium, cation exchange capacity and clay content was also registered from soil of the natural forest compared to the other land use types. The study further revealed that there was significant (p<0.05) difference in available phosphorus among the different land use types. However, there was no significant difference in silt fraction, sand, bulk density and exchangeable sodium under soils of different land uses. The results obtained from the study indicated that soils of grazing, cultivated land and plantation forest are strongly acidic (pH<5.5). Therefore, appropriate reclamation method should be lunched to improve agricultural productivity and sustainability of the study area.
Soundarapandian P, Dinakaran GK and Varadharajan D
Mass larval culture experiments were carried out from naturally collected berried females and also unilateral eyestalk ablated females. Fecundity was more in the naturally collected berried females. It was ranged between 7,271 ± 17.34 and 28,520.60 ± 31.11. Comparatively the fecundity was little bit low in the eyestalk ablated females. It was ranged between 7,112.66 ± 19.19 and 28,225.33 ± 36.37. The hatching rate was maximum in the naturally collected berried females (97.65 ± 0.59). It was less (92.81 ± 0.69) in the eyestalk ablated females. The incubation period for naturally collected females was 14.00 ± 0.07 days and it was 14.79 ± 0.11 days in eyestalk ablated females. The larval cycle was completed within 40.86 ± 0.58 days in naturally collected berried female. Whereas it was 41.97 ± 0.38 days in eyestalk ablated females. The survival rate of hatchlings was higher in naturally collected brooder (74.04 ± 0.09%) and it was less (70.35 ± 0.21%) in the eyestalk ablated females.
Taylor ET, Wirmvem MJ, Sawyerr VH and Nakai S
Eleven airborne PM2.5 PAH concentrations were characterized in the kitchen, outdoor and living room environments in households that burn wood and charcoal fuels in Western Sierra Leone, during a survey that was conducted in September 2011. The average concentration of total PAHs (Σ11PAHs) was 1279.7 ng/m3 in kitchen, 41.2 ng/m3 in outdoor, 19.8 ng/m3 in living room for households burning wood while those burning charcoal was 96.5 ng/m3, 13.1 ng/ m3 and 8.9 ng/m3 in the kitchen, outdoor and living room, respectively. The percentage contribution of higher molecular weight PAHs to Σ11PAHs was about 25% higher compared to medium molecular weight PAHs for either household category in all three locations, with a somewhat different scenario for kitchens with wood stove. The ratio of indoor/ outdoor air of Σ11PAHs showed considerable variation among households burning charcoal (p=0.0021; t-test) relative to those burning wood, attributed to non-prolonged equilibrium between the two environments. Benzo(a)pyrene (BaP) equivalency results revealed that BaP and dibenzo(a,h)anthracene were the two most dominant compounds that contributed to more than 90% of the total carcinogenicity in all three environments for households burning wood and charcoal. The results suggest that kitchens, where biomass fuels are burnt continue to be a hazardous place for people of developing countries to spend their time.
Priyadharsini S, Manoharan J, Varadharajan D and Subramaniyan A
The P. volitans generally is an edible fish, it protein are considered to be a source of food for human and the venom use for the development of new drugs. Pharmacological character of its venom were characterised during the study period. The lionfish venom shows the neuroprotective efficacy in alcohol intoxicated albino rat brain. These findings are further confirmed by histopathological observations. Therefore, the lionfish venom could be used as a neuroprotective agent.
Patricia Córdoba, María Eugenia González, Aixa González, Mercedes Maroto-Valer, Natalia Moreno, Noelia Sepúlveda, Rodrigo Navia and Xavier Querol
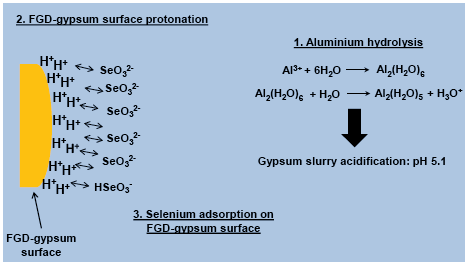
The use of a Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD)-gypsum as material for selenium removal in re-circulated waters from a wet limestone FGD system with water re-circulation to the scrubber and with use of an Al-additive, to increase SO2 emission abatement efficiencies, has been evaluated by adsorption studies. Potentiometric titration experiments for FGD-gypsum reveal that the acidic conditions of the aqueous phase of gypsum slurry, induced by the Al-additive, result in the protonation of the FGD-gypsum surface. The adsorption isotherms of Se onto FGD-gypsum are appropriately described by the Langmuir model suggesting that Se is adsorbed by the protons adhered on FGD-gypsum surface and forms a monolayer. The removal of Se from FGD waters by the employment of FGD-gypsum is significant as prevention measure based on the management on FGD-gypsum and water streams before their production and the subsequent disposal in landfills and/or in application scenarios.
Shilpy Sharma, David A Swayne and Charlie Obimbo
Modelling requires comparison of model outputs to measurements, for calibration and verification. A key aspect data smoothing is to “filter out” noise. Often, data must be adjusted to a model’s time step (e.g. hourly to daily). For noisy data, LOWESS/LOESS (Locally Weighted Scatterplot Smoothing) is a popular piecewise regression technique. It produces a “smoothed” time series. LOWESS/LOESS is often used to visually assess the relationship between variables. The selection of LOWESS tuning parameters is usually performed on a visual trial and error basis. We investigate the so-called robust AIC (Akaike Information Criteria) for automatic selection of smoothing. Robust Pearson correlation coefficient and mean-squared error are employed to determine the polynomial degree of piecewise regression. The exclusion of outliers is attempted using a Hampel outlier identifier. We illustrate, assuming noisy linear data, how our proposed methods work for auto-tuning both the smoothing parameter and the degree of polynomial for LOWESS/ LOESS.
Johnson Olayinka Olusola and Aiyesanmi Ademola Festus
The distribution and level of six heavy metals viz: Cr, Cd, Pd, Cu, Zn, and Ni in different organs gill, head, bone, muscle and eye of five fish species Arius latisculatus, Cynoglossus browni, Caranx lugubris, Sardinella aurita, Caranx senegallus, and associated water collected from the coastal waters of Ondo State, Southwestern Nigeria were investigated in this study. The concentrations of Zn (0.10-0.36 mg/kg), Cu (0.18-0.27 mg/kg), Ni (BDL-0.01 mg/kg) and Cr (0.04-0.63 mg/kg) found in the water samples were within the Maximum Permissible Level (MPL), while higher concentrations above the MPL were recorded for Cd (0.08-0.19 mg/kg) and Pb (0.34-0.79 mg/kg). Zn was the most abundant heavy metals found in all fish species organs investigated. Higher concentrations of the metals were recorded in the gills and eyes compared to other organs in most of the fish species. While the concentration of Zn (0.28 mg/ kg-4.14 mg/kg), Cu (BDL-5.72 mg/kg), Ni (BDL-0.01 mg/kg), and Cr (BDL-3.41) in the fish tissues were within the Maximum Allowable Level (MAL) for a food source, the findings of this study Cd (BDL-3.18 mg/kg) and Pd (BDL-1.14 mg/kg) showed values exceeding the maximum allowable level, thus constituting potential health hazard to consumers of these fish species. Transfer factors of most metals in fish from water were greater than or equal to 1 suggesting bioaccumulation of the metals by the fish from water column, while distribution of the heavy metals in the different fish parts were organ specific.
Almalih MA, Salih A, Dafaallah AA, Magid SAA, Gizouli AME and Tilal AS
It is a strategic target now to reuse treated industrial waste water for washing, irrigation etc., to efficiently manage and maximize Sudanese's water resources. The aim of the present work was to study the performance of natural zeolite (scolecite) for removing heavy metals from industrial waste water. Natural zeolite deposit sample was collected from Bayooda desert. Natural zeolite used (scolecite) was characterized by XRD, XRF, SEM and FTIR instruments. The physical properties (pH, EC, TDS, COD, BOD, total hardness) and chemical properties (Ni2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Fe3+, Cr3+) of the collected industrial waste water samples were investigated. Zeolite sorbed around 95.8, 88.1, 48, 50, 19.7 and 99.9% of Ni2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Fe3+ and Cr3+ metal concentrations respectively. According to the percentage sorption values, the selectivity sequence of studied metals by natural zeolite can be given as Cr3+>Ni2+
Mohsen Rezaei, Zahra Nazari Khorasgani, Azadeh Nakisa, Nima Imani, Saeid Rezaee, Mohammad Javad Khodayar and Heibatullah Kalantari
Background: Currently, release of highly toxic polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs) from combustion processes and industrial activities in the environment, their persistence and bioaccumulation in human attracted more attention and dairy products are among the most important sources of human exposure. This study was aimed to determine the most toxic congeners of dioxins in fresh cow’s milk samples collected from the Southwest of Iran. Materials and Methods: 15 composite samples of pasteurized milk from the each of 3 major dairy factories of Khuzestan Province in spring, summer and autumn from July 2011 to March 2012 (3 seasons) were collected. After precipitation of the proteins, fat phase was reduced and extracted with hexane and ether. After dehydration, furans existed in fat percolated with hexane through a column chromatography which contained silica gel/silver nitrate, silica gel, silica gel/sulfuric acid respectively and with percolating output through another column contained activated charcoal and silica gel and washing the lower column with a mixture of dichloromethane-hexane and toluene, concentrated and dissolved in mobile phase and analyzed using HPLC: 150 mm × 4.6 mm ID, 5 μm cosmosil 5 NPE column equipped with a UV detector at 254 and 267 nm, mobile phase:methanol/water (80:20, v/v) at flow rate of 1 ml/min. Results: All samples were found to be contaminated with dioxins comparatively. The concentration of 2, 3, 7, 8 TCDD and 1, 2, 3, 7, 8 PCDD in lipid content (2-3%) were detected in the range of 0.96-3.17 TEQ pg/g and 0.59-2.87 TEQ pg/g respectively. The mean concentrations of dioxins during summer were higher for all factories than other seasons and the lowest content were obtained during winter.
Beligh Mechri, Meriem Tekaya, Hechmi Cheheb, Mohamed Hammami and Faouzi Attia
The use of organic acids and phenolic compounds that are present in olive mill wastewater (OMW) represents a new perspective in rock phosphate (RP) research and a possible solution for the recycling of the OMW. To test the hypothesis that OMW applied in combination with Gafsa RP to olive tree plants can affect P mobilisation from RP to olive trees, a field experiment was conducted to evaluate the potential use of OMW with RP as soil amendment on olive tree alkaline soils. Treatment included three levels of OMW and RP application: M0 (non-amended control), M1PN (30 m3 ha-1 of OMW+150 kg ha-1 of RP) and M2PN (60 m3 ha-1 of OMW+150 kg ha-1 of RP). Five years after the start of the experiment, the available phosphorus decreased significantly. Amended olive trees had lower rate of photosynthates compared to the control, mostly due to decreased sink demand for carbon by the root. The biomass of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi and the development of colonisation in the olive tree roots decreased dramatically by the application of OMW and RP. Phenols accumulation in leaves was significantly higher in the OMW and RP amended soils, whereas total chlorophyll, chlorophyll a, and chlorophyll b in olive trees leaves decreased significantly after agronomic application of OMW and RP. Taken with data from experiments in field conditions, our results suggest that the use of OMW in combination with RP, in order to mobilise P from RP to olive trees, are expected to have a major negative impact on plant performance.
Adugna Boke, Negussie Megersa and Endale Teju
This study was designed to assess the levels of selected metals (Pb, Cu, Zn, Cd, Ni, Cr and Ca) in wild edible plants and their corresponding soil samples by FAAS. A wet digestion procedure has been adopted to digest the plant and soil samples. The validity of the method was evaluated by spiking the sample with a standard of the selected metals. The levels of Pb, Cd, Ni, Cu and Cr were below detection limits in all the edible parts of the studied plants except in the root of Eriosema cordifolium where Ni and Cr were detected. Similarly, only Ni, Cu and Cr were detected in the soil samples of Eriosema cordifolium and Physalis peruviana plants. But, Zn, and Ca were detected in all the studied samples and varied in the range 31.3-157.5 and 24.4-6214.3 mg kg-1 in plants and 55.4-149.8 and 367.1-6032.3 mg kg-1 in soil samples, respectively. However, the value of selected metals in soils and plants sample were lower than the permissible limit recommended by European Union Standard and Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives respectively with the exception of Zn in tuber of Pachyeymbium sacculatium plant.
Gopal Krishan, Singh RPand Tashi KS
In the present paper, the water levels data versus time plots for pre-monsoon and post-monsoon seasons over a period of 8 years 2006 to 2013 show a progressive decline at all the 13 observation points. During the 8 years (2006- 13), out of the total 13 blocks, groundwater level in 8 blocks declined during post-monsoon season and groundwater level increased in 4 blocks and no fluctuation was observed in 1 block. The maximum decline of -1.52 m was observed in Bhunerheri block of Patiala and the minimum decline of -0.09 m observed in Firozepur block. The groundwater level showed a maximum increase of 0.91 m in Mamdot block. In Patiala district, the depth of water level is very high in comparison to the other districts. A strong positive correlation existed between groundwater levels in all the blocks of Patiala to groundwater levels in Kotkapura and moderate to good positive correlation with the groundwater levels in Firozepur, Guruharsarai and Pakhowal because of the extensive and laterally continuous aquifer in these blocks. However, the declines are not very sharp at Faridkot and Machivara stations because there is a gain of subsurface recharge through canal seepages in the areas where these observation wells are located.